Benefits of Spring Boot's application.yml file with examples
What are the two Spring Boot file formats?
Spring Boot allows developers to configure their applications using one of two formats:
- The traditional
application.propertiesfile. - The newer
application.yamlfile.
Fundamentally, these two file formats provide the exact same functionality. Any property that can be configured within the application.properties file can also be configured in the application.yaml file. From that standpoint, the two formats are identical.
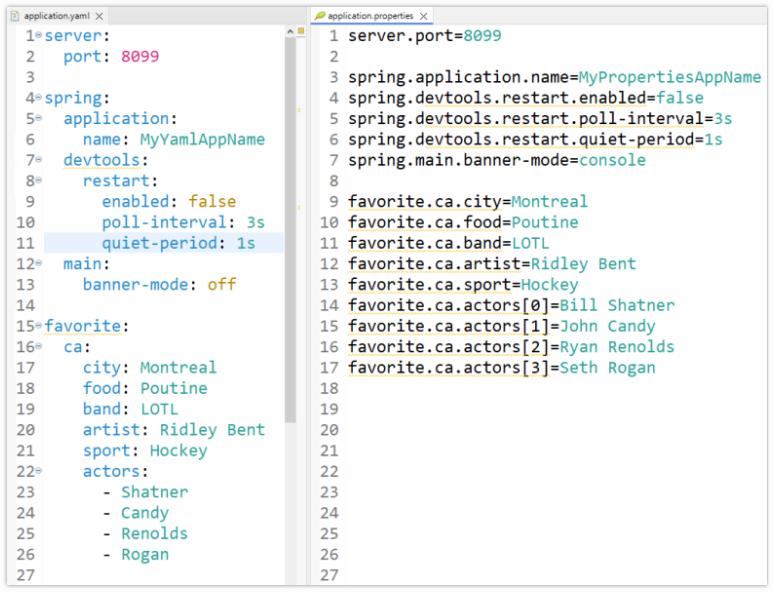
Spring application.yml file example
Here is a simple application.yaml file that configures:
- An external resource (ports on a Tomcat server).
- The Spring framework itself.
- Custom properties added by the developer.
server:
port: 8099
spring:
application:
name: MyYamlAppName
devtools:
restart:
enabled: false
main:
banner-mode: off
favorite:
ca:
city: Montreal
actors:
- Bill Shatner
- John Candy
Spring YAML vs. properties
When compared to the traditional application.properties file, YAML files are easier to read and have less repetition.
The following application.properties file configures all of the same properties as the application.yaml file above, although most people would find the YAML file above easier to read:
server.port=8099 spring.application.name = MyPropertiesAppName spring.devtools.restart.enabled = false spring.main.banner-mode = console favorite.ca.city = Montreal favorite.ca.actors[0] = Bill Shatner favorite.ca.actors[1] = John Candy
What are the Spring YAML config disadvantages?
As far as describing data goes, there is no functional difference between the YAML and properties formats. Both formats can describe properties equally well.
However, in the current version of Spring Boot, you cannot inject properties from a YAML file using the @PropertySource annotation.
For example, this code will compile, but at runtime the properties in the favorites.yaml file will not be resolved:
@PropertySource("classpath:favorites.yaml")
What are the benefits of Spring Boot YAML files?
If we overlook the @PropertySource limitation, YAML should be the preferred configuration format for new Spring Boot projects. The key benefits of YAML-based Spring Boot configuration files includes the following:
- Improved readability.
- JSON compatibility, as YAML is a superset.
- Access to advanced YAML features such as anchors and aliases.
- Consistency throughout the DevOps stack, as tools like Docker and Kubernetes all use YAML.
Can you use Spring properties and YAML files together?
Fortunately, developers aren’t forced to choose between YAML and properties-based Spring configuration. The two formats can be used together. If the same property is defined in both files, the YAML file loses and the traditional properties file wins.
Either way, the true winner is the developer who has the flexibility to choose the Spring Boot application configuration file format that works best for them.
Cameron McKenzie is an AWS Certified AI Practitioner, Machine Learning Engineer, Solutions Architect and author of many popular books in the software development and Cloud Computing space. His growing YouTube channel training devs in Java, Spring, AI and ML has well over 30,000 subscribers.