Profiles, Spring Boot and application properties files
Spring profiles make the development of environment-specific configurations effortless.
- Need to customize logging in your dev environment? Spring profiles handle it.
- Testing locally with H2 but using MySQL in production? Spring profiles handles it.
- Want to make Java apps run faster than natively compiled C? Well, Spring profiles can’t do that. There are limits.
Profile-based Spring configurations
To set up a custom profile, create an application.properties file with the profile name appended after a dash. For example, files for dev, prod and UAT environments would look like this:
-
application-dev.properties
-
application-uat.properties
-
application-prod.properties
Simply add your custom configurations to the corresponding, profile-specific properties file, and those configurations will be used when the given profile is active.
Multi-profile YAML and properties support
If creating multiple application.properties files is too much of a burden, you can alternatively place all of your configuration in a single file. Just separate each profile section with a #---.
Here’s an example of an application.properties file supporting dev, UAT and prod:
How to activate a Spring profile
The active Spring profile is initially set through the spring.profiles.active property in the application.properties file:
spring.profiles.active=dev
However, this can be easily overridden at runtime by setting the active profile through an environment variable passed to the JVM at startup.
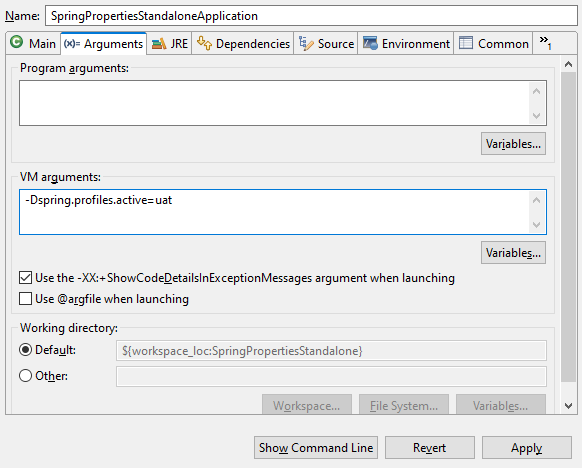
- In Eclipse, the active Spring profile can be set through the VM argument in the configuration tab.
- In Docker, the active Spring profile can be set by configuring the
envfile passed to the container at runtime. - In Kubernetes, the active Spring profile can be set by adding an environment variable.
Spring profiles make it easy to alter your application’s behavior as it moves from one environment to another, simply by changing the spring.profiles.active property as needed.
Profiles, YAML and the @Profile annotation
Editing the application.properties is the easiest way to get started with Spring profiles, but that’s just the tip of the iceberg. Spring profiles also support YAML configurations and, through the @Profile annotation, they can change the way Spring performs dependency injection at runtime as well.
Spring profiles are a powerful and flexible tool for Java developers building scalable, enterprise-grade applications. Whether it’s customizing configurations or altering IoC behavior across environments, Spring profiles make the process simple and efficient.