How to git push an existing project to GitHub
How do you add an existing project to GitHub?
There are two ways to add an existing project to GitHub:
- The easy way: Clone a GitHub repo and copy existing project files.
- The proper way: Invoke git init and git remote add commands to update remote references.
I’m going to show you both ways to do it, and I promise you, using the easy way is going to save you a lot of time eliminate a lot of frustration. Let’s start with that approach first.
Add a project to GitHub the easy way
The following approach isn’t the documented, academically endorsed approach to add a local project to a remote GitHub repo.
Nevertheless, it’s easy, it works and it doesn’t have any negative ramifications other than a large copy and paste.
To quickly add your project to an existing GitHub repo, just follow these steps:
- Create a new GitHub repo that contains a README file.
- Use Git to clone the GitHub repo locally.
- Copy your project files into the folder created by the clone.
- Perform a git add . and a git commit.
- Push your changes up to GitHub.
Copy and push benefits and drawbacks
That’s it. That’s how easy it is to add an existing project on your filesystem to GitHub.
The benefit of this approach is that you can also add your project to a GitHub repo that already has files in it.
The generally prescribed method to add a project to an existing GitHub repo typically assumes the repository is blank. If the existing GitHub repo is not blank, you must dangerously push your project to GitHub with the force flag.
The drawback is that the location of your project on your filesystem changes, but that’s easily addressed with another copy and paste.
Personally, I like the easy approach.
Next, I’ll describe the alternate approach, which adds a remote reference to the GitHub server in your existing project’s config files.
Proper steps to add existing code to GitHub
The proper way to push a new project into an existing GitHub repository follows these steps:
- Create a GitHub repository for the existing project.
- Copy the GitHub URL for the new repo to the clipboard.
- Perform a
git initcommand in the root folder of the existing project. - Add all of the existing project’s files to the Git index and then commit.
- Add the GitHub repo as a remote reference for the existing project.
- Perform a
git pushoperation with the-uand-fswitches. - Verify that the existing project’s files have been pushed to GitHub.
How to push code to GitHub
Many certified DevOps engineers and professional solutions architects only want to know the Git commands necessary to push their existing project to GitHub.
| Git, GitHub & GitHub Copilot Certification Made Easy |
|---|
| Want to get certified on the most popular AI, ML & DevOps technologies of the day? These five resources will help you get GitHub certified in a hurry.
Get certified in the latest AI, ML and DevOps technologies. Advance your career today. |
To save those readers from going through the entire example, here are the Git commands used in this tutorial. These commands assume a push to a GitHub repo named existing-website, owned by a GitHub user named cameronmcnz:
git initgit add .git commit -m "Add existing project files to Git"git remote add origin https://github.com/cameronmcnz/example-website.gitgit push -u -f origin master
Updating a remote GitHub repo
To push an existing project to GitHub, you must first create a GitHub repository. To do this, simply click the green “Create repository” button in GitHub’s online console and provide a repository name.
For this example, we will name the repository example-website.
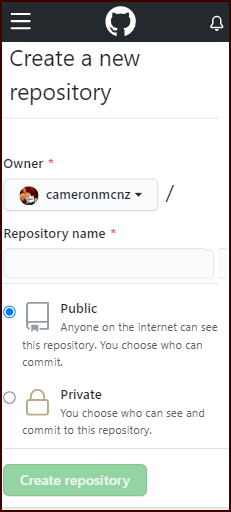
You must create a GitHub repo to manage your existing project’s files.
Obtain the repo’s GitHub URL
After you create the repository, click the green “Code” button. This reveals the GitHub URL for HTTPS connections.
Copy this value for use in a future step.
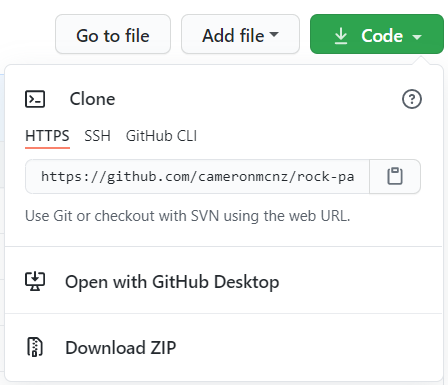
The GitHub URL is used to push the existing project to GitHub.
Initialize Git in the existing project
If the existing project does not already use Git, issue a git init command in the root folder. After the repository is initialized, add all of the project files to the Git index and perform a commit:
git add . git commit -m "Add existing project files prior to the push to GitHub."
Add a remote reference for GitHub
To let your existing project synchronize with GitHub, issue a git remote add command to configure a reference from you local Git installation to the repository on GitHub. Note that the last segment of the git remote add command is your project’s GitHub URL.
git remote add origin https://github.com/cameronmcnz/example-website.git
Push the first commit to GitHub
Once you’ve added the remote reference, you are ready to push your existing project to GitHub.
Simply issue a git push command with the name of the current branch along with the -u and -f switches.
Note that older Git repositories create a master branch by default, while newer ones use main. Amend the git push command accordingly.
git push -u -f origin master
The -u switch makes the remote GitHub repo the default for your existing project. The -f switch forces Git to overwrite any files that already exist on GitHub with your existing project’s files.
Verify the GitHub push
To verify that the existing project was pushed to GitHub successfully, log into the GitHub website and browse the repository. All of the files from your existing project should be visible on GitHub.
And that’s how easy it is to push an existing project to a Git or GitHub repository.
Cameron McKenzie is an AWS Certified AI Practitioner, Machine Learning Engineer, Solutions Architect and author of many popular books in the software development and Cloud Computing space. His growing YouTube channel training devs in Java, Spring, AI and ML has well over 30,000 subscribers.
Next Steps

The AWS Solutions Architect Book of Exam Questions by Cameron McKenzie
So what’s next? A great way to secure your employment or even open the door to new opportunities is to get certified. If you’re interested in AWS products, here are a few great resources to help you get Cloud Practitioner, Solution Architect, Machine Learning and DevOps certified from AWS:
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Book of Exam Questions
- AWS Certified Developer Associate Book of Exam Questions
- AWS Certified AI Practitioner Book of Exam Questions & Answers
- AWS Certified Machine Learning Associate Book of Exam Questions
- AWS Certified DevOps Professional Book of Exam Questions
- AWS Certified Data Engineer Associate Book of Exam Questions
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Book of Exam Questions
Put your career on overdrive and get AWS certified today!




